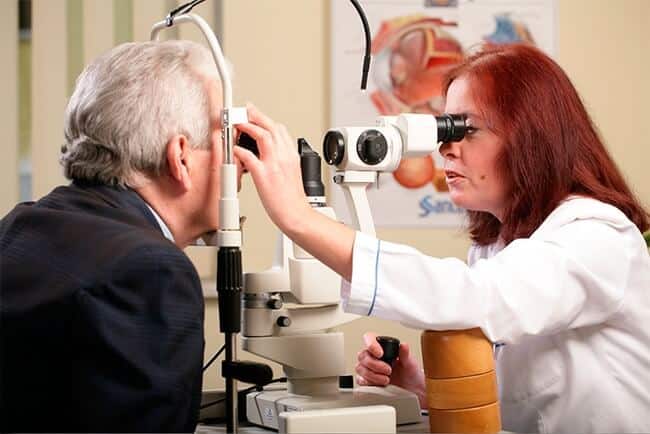
Cataract diagnostics. Just to get a better understanding, the crystalline lens is the eye’s natural lens, which consists mostly of protein and water. Normally, the crystalline lens is clear. But some external or internal factors can cause the lens to lose its transparency, which means the onset of cataract.
Cataract diagnostics
It is essential to undergo medical consultation with a specialist once a year after the age of forty to diagnose the disease in time and to prevent the development of serious visual pathologies. In this case, you should see an ophthalmologist. Cataract diagnostics shall be performed during a complex eye exam with a dilated pupil. The doctor examines the crystalline lens with a biomicroscope (slit lamp) and detects possible opacities.
You can get quality cataract diagnostics in Kyiv and Odesa, Ukraine, and detect serious conditions at the specialized Eximer Ophthalmology Clinic.
Congenital cataract diagnostics
Unfortunately, cataract is a disease that affects both adults and children starting from birth. Children may be born with congenital cataracts or develop this disorder during the first year of life. Congenital cataracts can occur in one or both eyes.
Why it is so crucial to identify and treat congenital cataracts as early as possible? First, a child with cataracts cannot see well and does not develop binocular vision. Second, the child lags in development since the coordinated work of the brain and eyes is disturbed. Third, the infant cannot control eye movement, which leads to the development of strabismus.
Cataract early diagnostics
The development of a child with a congenital cataract depends on how quickly the disease is detected. This is why timely examination by an ophthalmologist is so vital, especially for those children who are at risk.
Congenital cataracts can be detected in an infant if:
- There is a family history of congenital cataracts;
- The baby is born prematurely;
- Was infected before or shortly after birth;
- The expectant mother has had an infectious disease, such as chickenpox, cytomegalovirus, rubella, toxoplasmosis, etc.
It is worth noting that many children with congenital cataracts have no other pathology.
What are the signs and symptoms of congenital cataracts?
When affected, the pupil of the baby’s eye looks gray or white rather than black. It may appear as if it is covered by a film, or there may be a spot on the pupil.
Doctors often diagnose congenital cataracts when examining a baby after birth. Sometimes parents may notice that one of their child’s eyes looks unusual. If this is the case, it is worthwhile for the baby to be examined by an ophthalmologist using an ophthalmoscope, biomicroscope, and mydriasis (dilated pupil).
WARNING! If you are concerned about any of the above symptoms in your baby or anything that makes you wary, be sure to have your baby examined by an ophthalmologist.
Diagnostic methods
Cataract exams in patients must be very thorough, using modern equipment and the latest technology, and pupil dilation is a must. Many people confuse the development of cataracts with other conditions, so trust your vision to an experienced ophthalmologist.
The doctor will examine your medical history, ask about the complaints that bother you, and perform a series of examinations.
Routine (standard) diagnostic methods
Visual acuity test or visometry.
The visual acuity test involves a chart with symbols or letters to determine how well you see the signs. Your eyes are tested one at a time, first closing one eye and then the other and asking you to read the larger symbols first, and then the smaller ones. This test allows suspecting signs of visual impairment.
Slit lamp examination (biomicroscopy).
The slit lamp allows the ophthalmologist to see the front structure of the eye under magnification. It helps examine the cornea, iris, lens, and conjunctiva. And the biomicroscope allows the doctor to see these structures in small sections, making it easier to detect any tiny anomalies.
Eye ground exam or ophthalmoscopy.
To prepare for the eye ground exam, the patient is given drops to dilate the pupils. This makes it easier to look at the back of the eye (retina). Using a slit lamp or a special device called an ophthalmoscope, the doctor can check the lens for signs of cataracts.
Additional or special methods of cataract diagnostics
When signs of cataracts are detected, the ophthalmologist prescribes additional examinations to confirm the diagnosis and check the eyes for other possible conditions.
Visual field exam or perimetry.
This exam is performed with a special perimeter device. It allows determining the eye sensitivity, the presence of optic nerve atrophy, and how well the peripheral vision is preserved. This test is performed alternately: on one eye and then on the second eye. The patient closes one eye and looks at the screen of the device, observing flashes in different points. When such a flash is detected, the person has to press the corresponding button. The device saves the findings and then gives the result.
Intraocular pressure measurement.
This is a contact-free test with a modern pneumatic tonometer. It allows measuring the intraocular pressure, which can indicate the onset of glaucoma
How do I know if I have a cataract?
Cataract development is defined by the opacity of the protein inside the crystalline lens. Consequently, the light transmission is impaired, the image may be distorted, or the color vision may change. In fact, such complaints indicate the onset of cataracts:
- A person’s vision gets worse, and it becomes more difficult to cope with the usual strain of reading or driving a car.
- Image quality may be significantly impaired in bright light.
- As the color of the lens changes, color perception is altered as well, and objects can increase in number. That is, when looking at a bright source of light, such as the moon or stars, their number can increase up to sixteen times.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should definitely consult an ophthalmologist.
Some tips on when to go to the clinic
There is no separate advice on what to do if cataract, glaucoma, or macular dystrophy is suspected. There is one general piece of advice, as it is followed in a civilized society: every person over forty years of age should undergo a medical consultation (in this case, an ophthalmologist) once a year. If you notice unusual symptoms of vision deterioration, then you should not wait for total blindness. Any disorder, including cataracts, is easier to cure at an early stage. Therefore, at the first symptoms, we recommend scheduling an appointment with an ophthalmologist for diagnosis and consultation.
Differential diagnosis of cataract
A cataract develops gradually. First, the vision deteriorates, the image becomes blurred and unclear, objects become double, and so on up to total blindness. The differential diagnosis of cataract allows determining the stage of cataract development:
Differential diagnosis of immature cataract
In an immature cataract, the crystalline lens increases greatly in size, but the anterior part of the lens may remain relatively clear. Intraocular pressure increases due to lens swelling. The patient may complain of a fogging sensation in front of the eyes. Color perception is impaired.
Differential diagnosis of mature cataract
In a mature cataract, the lens becomes opaque, taking on a bluish-white tint. Object vision gradually deteriorates to the point where the person can see almost nothing and can only detect light.
Differential diagnosis of complicated cataract
Complicated cataract results from other concomitant conditions such as diabetes mellitus, uveitis, high myopia, glaucoma, rheumatoid arthritis, retinal dystrophy, etc. Symptoms of complicated cataracts may include visual impairment, blurred vision; pupil discoloration, photophobia, double vision, etc.
Benefits of cataract diagnostics at Eximer Ophthalmology Clinic
standards
treatment
quality
vision

and comfortable
treatment

period
rehabilitation
A cataract is a serious eye condition that can eventually lead to blindness, so it needs to be diagnosed and treated in a specialized ophthalmology clinic.
Cataract diagnostics at Eximer Ophthalmology Clinic has several key advantages:
- During the examination, the doctor diagnoses the entire visual system, ruling out the onset of other concomitant vision disorders.
- All eye exams are contact-free, observing preventive safety precautions.
- The latest high-quality devices are used for diagnostics, which have proven their efficiency in making the right diagnosis.
- Only experienced ophthalmologists consult and make a diagnosis based on the examination data.
- Cataract diagnosis is painless and does not cause any discomfort to the patient.
You can schedule an appointment for a cataract diagnosis online at the clinic’s website or by calling us.